Spotlights
CNC Machinist (Computer Numeric Controlled Machinist), CNC Machinist (Computer Numerically Controlled Machinist), Gear Machinist, Machine Repair Person, Machinist, Maintenance Machinist, Manual Lathe Machinist, Production Machinist, Tool Room Machinist
Modern society is in love with products, both large and small. From cars to computers, we can’t live without our manufactured goods. And without CNC Machinists and Operators, many (if not most) of the products we use and often rely on wouldn’t exist. These skilled tradespeople use a variety of computer numerically controlled (CNC) machines and equipment to produce a wide range of precision metal parts.
Machinists and Operators have similar duties, but Machinists have more experience and may supervise Operators. They input instructions into the CNC machine they’re working with to ensure the parts are cut and crafted as needed. They may produce one specific part over and over, or have a set of parts they need to make batches of each day. In some cases, their job is to repair or replace a broken part.
CNC machines can be very dangerous to work with, which is why CNC Machinists and Operators must be highly trained in their proper usage. In addition to using these machines, Machinists and Operators may also utilize lasers and electrified wires as they work, adding even more risk into the equation! This makes it even more imperative to strictly follow safety protocols. It’s also why most employees in this trade learn their skills through a combination of academic courses and supervised apprenticeships.
- Making parts that are vital to the completion of much-needed products
- Contributing to the overall economy by providing a steady stream of parts used in almost all industries
- Plenty of independence, for those who don’t enjoy customer-facing jobs or roles with a lot of managerial oversight
Lịch làm việc
CNC Machinists and Operators work full-time, with overtime necessary depending on goals and timeframes. Their duties are usually performed indoors in factories or shops, but work may require them to travel to various locations to do on-site repairs.
Nhiệm vụ tiêu biểu
- Discuss final product needs and costs of producing them in the desired quantities
- Review reference files (blueprints, drawings, etc.) and written descriptions and specifications of desired parts and items to be made
- Create new work sketches
- Determine the order of sequence of the work process before starting
- Use measuring instruments to determine the dimensions of the final fabricated pieces
- Verify the tolerance of materials to be machined
- Use computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) programs, as needed
- Set up, program, and operate computer numerically controlled (CNC) machine tools to make, or machine, precision parts
- Ensure program updates are compatible with CNC machines
- Adjust various components of CNC machines, such as cutting blades, holding fixtures, etc.
- Determine the type of blanks to use in creating a specified workpiece
- Mark metal stock where cuts will be made
- Mang thiết bị bảo vệ cá nhân cần thiết và tuân theo các quy trình an toàn đã thiết lập
- Keep an eye on CNC machine feeds and speeds
- Tạo các bộ phận bằng cách sử dụng các quy trình như tiện, phay, khoan, tạo hình và mài
- Screen items after cutting for defects and quality. Make adjustments to machinery, if necessary
- Diagnose machine errors and make minor repairs. Disassemble as needed
- Verify that completed products comply with requirements
- Remove waste material from workspaces and recycle or dispose of it properly
Trách nhiệm bổ sung
- Luôn cập nhật hướng dẫn kỹ thuật
- Train and mentor new CNC Machinists and Operators, technologists, and technicians
- Giữ khu vực làm việc sạch sẽ và thực hiện bảo trì định kỳ trên máy móc
- Discuss technical issues with the appropriate personnel
- Offer advice during the project planning phase, if asked
Kỹ năng mềm
- Sự tỉnh táo
- Phân tích
- Thận trọng
- Định hướng tuân thủ
- Tư duy phản biện
- Định hướng chi tiết
- Kỷ luật
- Kiên nhẫn
- Lập kế hoạch và tổ chức
- Kỹ năng giải quyết vấn đề
- Phán đoán đúng đắn
- Stamina
- Làm việc theo nhóm
- Quản lý thời gian
Kỹ năng kỹ thuật
- Machinist programs such as Armchair Machinist and Machinists’ Calculator
- Computer-aided design programs like Autodesk AutoCAD, CATIA, PTC Creo Parametric, and SolidCAM
- Phần mềm sản xuất hỗ trợ máy tính như Autodesk Fusion 360 và CNC Mastercam
- Phần mềm điều khiển công nghiệp như EditCNC hoặc Mazak Mazatrol
- Các chương trình quản lý thủ tục như Hexagon Metrology PC-DMIS
- Familiarity with tools and equipment such as micrometers, vernier calipers, lathes, milling machines, shapers, and grinders, drilling machines, cutting tools, lasers, and water jets
- Làm quen với các quy trình như gia công kim loại, hàn, xử lý nhiệt và hàn
- Làm quen với hệ thống thủy lực, hệ thống dây điện, chất bôi trơn và pin
- Familiarity with various types of metal and metal alloys, including steel, brass, aluminum, copper, zinc, lead, vanadium, and manganese
- Employment services
- Sản xuất máy móc
- Machine shops
- Sản xuất thiết bị vận tải
CNC Machinists and Operators are relied on to mass-produce products that conform to very specific requirements. Thus their work must be meticulous, even under pressure to meet deadlines. They have to take into consideration multiple factors, including what metals to use and how best to cut or shape them. Factories can be loud and dangerous, requiring workers to wear protective gear, such as goggles and hearing protection.
They need to carefully follow safety procedures to avoid injury to themselves or others in the area. The day-to-day job requires plenty of stamina because workers are usually on their feet, often in a bent or leaning positions. The repetition of machining parts can get monotonous after a while, but workers have to keep their focus because of the inherent hazards of the job. There can be long periods of working alone, so Machinists sometimes need to look beyond their place of employment for socializing.
There are many CNC machine trends shaping the future of the industry. One is the development of machines capable of higher speeds, including faster spindle speeds, faster feed capacity, faster computing, and faster tool changing. These increases don’t diminish precision, because CNC machines are getting more accurate at the same time!
Along with these advancements, 3D printing is starting to share some of the workloads to make parts that CNC machines finish. Another change is the use of digital twins which “duplicate a CNC machine and its environment, including its setup on the shop floor, within the CAM software, providing accurate toolpath simulation” in order to “reduce or eliminate any surprises that may occur during the machining process.”
People who get into machine-related career fields usually enjoy working with their hands and feel comfortable using tools and stationary heavy equipment. They might have enjoyed math and computer programming courses in high school or liked doing projects in shop classes.
Machinists can collaborate with others but don’t mind being on their own for long periods. They might have been very independent growing up and may have always wanted a job where they have some freedom to do their work without a lot of interaction with others.
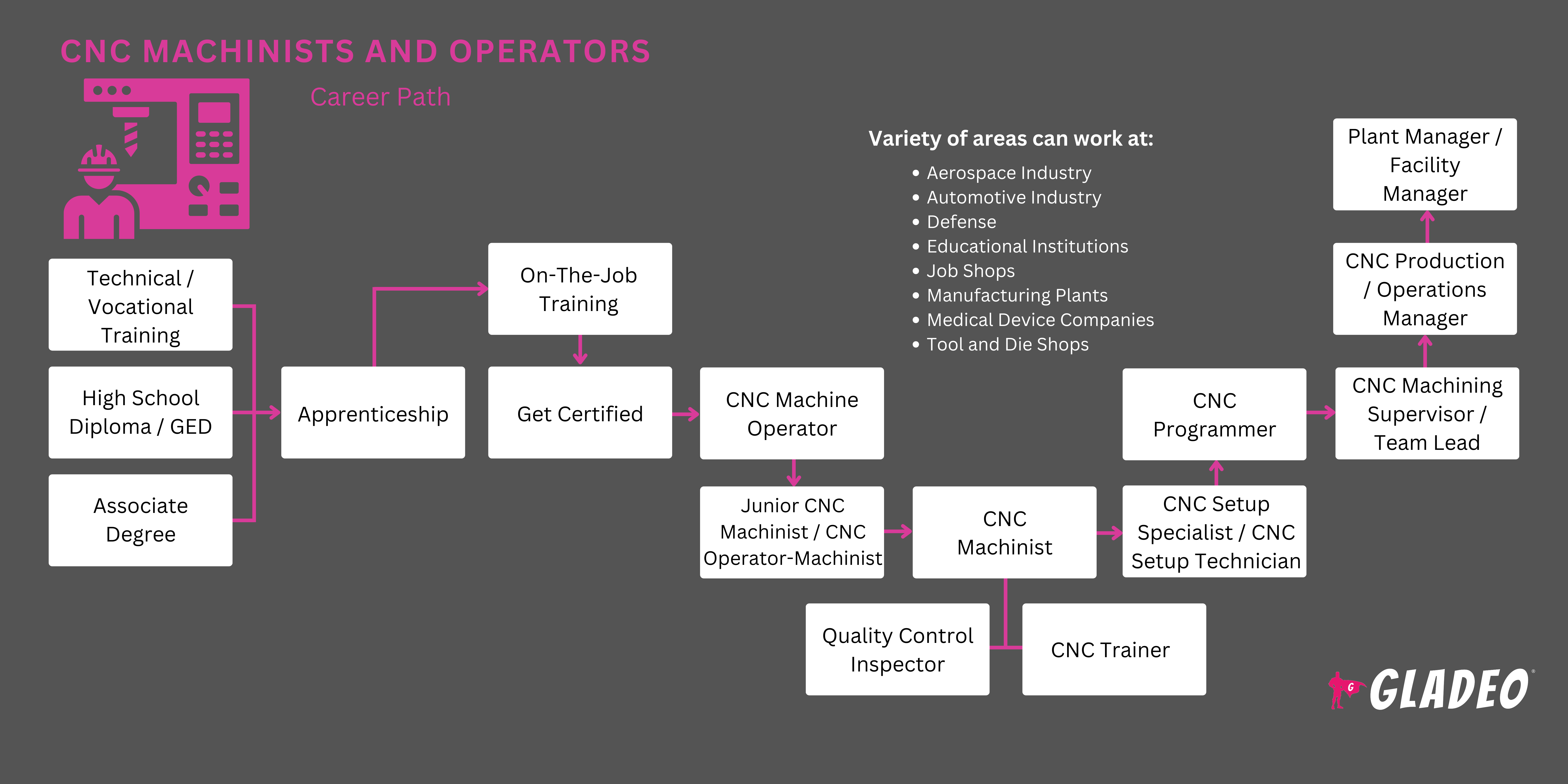
Giáo dục cần thiết
- CNC Machinists and Operators need at least a high school diploma or GED
- Many workers in this field pursue a certificate or associate’s degree at a community college or technical school where they brush up on their math skills and learn how to read blueprints, work with metal, use hand tools and CAD or CAM programs, and how to operate CNC machines
- Các khóa học phổ biến khác bao gồm:
- Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing
- Multi-axis milling and turning
- Precision measurement
- Chương trình
- An toàn cửa hàng
- Taking formal education classes prior to applying for jobs isn’t necessary, but can help make you more competitive during your job search
- Candidates with more qualifications may have better luck finding jobs where they can then learn remaining skills via On-the-Job training
- They might also land a sponsored supervised apprenticeship!
- Note, workers who are learning OJT or via apprenticeships may still be required to take classes outside of duty hours, to supplement what is being learned at work
- Optional certification programs can help Machinists and Operators qualify for advancement. Below are just a few of the certifications options out there:
- Association of Energy Engineers - Certified Measurement and Verification Professional
- International Council for Machinery Lubrication - Level I Machine Lubricant Analyst
- International Fluid Power Society - Fluid Power Engineer
- National Institute for Metalworking Skills -
▸ CAM Turning I
▸ CNC Lathe Operations
▸ CNC Lathe Programming Setup & Operations
▸ Machining Level I - CNC Milling: Operations
▸ Machining Level I - Drill Press I
▸ Machining Level I - Grinding I
▸ Machining Level I - Job Planning, Benchwork, and Layout
▸ Machining Level I - Measurement, Materials and Safety Job
▸ Machining Level I - Milling
▸ Machining Level I - Turning I (Chucking Skills)
▸ Metalforming Level I
▸ Certified Metalworking Fluids Specialist
▸ Oil Monitoring Analyst I
▸ Certified Oil Monitoring Analyst II
▸ There are also manufacturer and software-specific certs available!
- CNC Machinists and Operators don’t need to attend a four-year university, but decide if you want to complete a certificate or associate’s at a technical school or community college
- Xem xét chi phí học phí, giảm giá và các cơ hội học bổng địa phương (ngoài viện trợ liên bang)
- Think about your schedule and flexibility when deciding whether to enroll in an on-campus, online, or hybrid program. Many relevant courses may need to be done in-person to get hands-on experience
- Xem lại số liệu thống kê việc làm của chương trình dành cho sinh viên tốt nghiệp
- Check out Stecker Machine’s What is a CNC Operator? article for a great overview of the day-to-day
- Đăng ký nhiều môn toán (số học, đại số, hình học và lượng giác), vật lý, khoa học máy tính, khoa học vật liệu và các lớp học cửa hàng ở trường trung học
- Hãy cân nhắc việc học về bản vẽ cơ khí và đọc bản thiết kế thông qua việc tự học
- Tham gia các lớp học trực tuyến đặc biệt từ Coursera , Udemy hoặc các trang web khác
- Enroll in a community college or vocational/technical school program to learn CNC machining
- Tham gia một chương trình thể dục có thể giúp bạn tăng cường sức mạnh và sức bền
- Get some real-world job experience via part-time jobs related to machining or shop work
- Xem lại trước các tin tuyển dụng để xem các yêu cầu trung bình là gì
- Request to do an informational interview with a working CNC Machinist or Operator to learn about their jobs
- Theo dõi các địa chỉ liên hệ có thể đóng vai trò là người giới thiệu công việc trong tương lai
- Study books, articles, and video tutorials related to CNC machining tools, programs, and processes
- Tham gia vào các diễn đàn trực tuyến để đặt câu hỏi và học hỏi từ các chuyên gia dày dạn kinh nghiệm
- Engage with professional organizations to learn, share, make friends, and grow your network (see our list of Resources > Websites)
- Bắt đầu tạo sơ yếu lý lịch sớm. Tiếp tục thêm vào nó khi bạn tiếp tục, để bạn không bị mất dấu bất cứ điều gì
- Hãy xem các cổng thông tin việc làm như Indeed , Simply Hired , Glassdoor và Craigslist
- Get some practical shop work experience under your belt before applying, if possible
- Seek out apprenticeships sponsored by employers, unions, or trade associations
- Ask working CNC Machinists and Operators for job-seeking tips
- Get a certificate or associate’s degree. It isn’t always needed to get started but may put you ahead of the competition
- According to O*Net, about 33% of Machinists have a post-secondary (after high school) certificate, and 17% have “some college, no degree.” The rest are working with just their high school diploma or GED
- Hãy hỏi trung tâm hướng nghiệp của trường bạn để được trợ giúp kết nối với các nhà tuyển dụng và hội chợ việc làm
- Hỏi trước những người tham khảo tiềm năng để xem họ sẽ giới thiệu bạn hay viết thư giới thiệu
- Check out Machinist resume templates and review Machinist job interview questions
- At interviews, be honest and show a motivated attitude and eagerness to learn
- Expect to start out in entry-level CNC Operator roles then work your way up to CNC Machinist positions
- Pay close attention during OJT and any classes the employer sends you to
- Stay positive and motivated. Do solid work, follow procedures, and stay safe
- Demonstrate that you can be trusted to work independently. Set the example for others to follow
- Knock out relevant certifications to enhance your skills
- Ask your supervisor how you can improve your knowledge and skills to better serve the company
- Study manufacturer and software guides. Become the go-to expert and make yourself invaluable
- Learn all you can from those with more experience (but also keep in mind to follow procedures as directed by your employer)
- Keep your cool under pressure, and treat everyone with respect
- Collaborate effectively on teams, stay focused, and demonstrate leadership
- Train new workers thoroughly. Their mistakes could reflect back on your training
- Stay engaged with professional organizations and unions, such as the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers
Các trang web
- Hiệp hội các nhà xây dựng khuôn mẫu Hoa Kỳ
- Hiệp hội Công nghệ Sản xuất
- Hiệp hội kỹ sư năng lượng
- Hiệp hội nhà chế tạo & nhà sản xuất, quốc tế
- Hiệp hội thợ máy và công nhân hàng không vũ trụ quốc tế
- Hội đồng quốc tế về bôi trơn máy móc
- Hiệp hội năng lượng chất lỏng quốc tế
- Viện sản xuất
- Viện Kỹ năng gia công kim loại quốc gia
- Hiệp hội Dụng cụ và Gia công Quốc gia
- Hiệp hội sản phẩm gia công chính xác
- Hiệp hội tạo hình kim loại chính xác
- Hiệp hội các nhà nghiên cứu tribologists và kỹ sư bôi trơn
Sách vở
- Workholding for Machinists, by Tim Stevens
- Machinists’ Ready Reference, by C. Weingartner and Jim Effner
- Math for Machinists, by Mark W. Huth
Laboring in a shop or factory on CNC machines can be tiring, monotonous, or even lonely work. Many people enjoy it, but it’s not a job for everyone. If you’re interested in exploring similar occupations, the Bureau of Labor Statistics suggests the following:
- Nhà sản xuất nồi hơi
- Cơ khí máy móc công nghiệp, công nhân bảo trì máy móc và millwrights
- Công nhân máy kim loại và nhựa
- Thợ hàn, máy cắt, máy hàn và máy hàn
In addition, O*Net features these careers:
- Lathe and Turning Machine Tool Setters, Operators, and Tenders, Metal and Plastic
- Milling and Planing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders
- Multiple Machine Tool Setters, Operators, and Tenders
- Tool and Die Makers
Nguồn cấp tin tức
Việc làm nổi bật

Các khóa học và công cụ trực tuyến

Kỳ vọng về mức lương hàng năm
New workers start around $45K. Median pay is $56K per year. Highly experienced workers can earn around $66K.





